Symptoms of A Tooth Cyst and the Importance of Early Diagnosis
Symptoms of A Tooth Cyst and the Importance of Early Diagnosis
- 27 March 2024
- 39748 views
Symptoms of tooth cyst and the importance of early diagnosis. Get information about early intervention and treatment options for a healthy smile.
This content is for informational purposes only and does not replace medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Please consult a healthcare professional for any health concerns.
Table of Contents
A tooth cyst is a fluid-filled sac that forms in or around the tooth roots. These cysts can often be painless or have mild symptoms. Therefore, early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment.
What Are the Symptoms of a Tooth Cyst?
The symptoms of a tooth cyst generally include the following:
- Pain or Sensitivity: The cyst can exert pressure on surrounding tissues, causing pain or sensitivity in the tooth. This symptom usually indicates that the tooth cyst is growing or infected.
- Swelling or Lump: When tooth cysts exert pressure on surrounding tissues, swelling can occur on the jaw or around the gums. It may feel like a lump on the gum.
- Changes in Tooth Color: There may be changes in the color of the tooth in the area with the tooth cyst. The tooth may appear yellowish or gray.
- Gum Problems: A tooth cyst can cause gum recession or gum inflammation, leading to gum problems.
- Bad Breath or Taste: When a tooth cyst becomes infected, it can cause bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis
Factors highlighting the importance of early diagnosis of tooth cysts include the following:
- Preventing Complications: Early diagnosis can prevent complications that may arise due to a tooth cyst. As the cyst grows, it can exert pressure on surrounding tissues and lead to various problems.
- Expanding Treatment Options: Early diagnosis can expand treatment options. While a small cyst may be monitored without surgical intervention, large or infected cysts usually require surgical intervention.
- Reducing Pain and Discomfort: Early diagnosis can reduce a patient's pain and discomfort. A small cyst is generally painless. However, when it grows or becomes infected, it can cause pain.
- Preventing Other Dental and Jaw Problems: A tooth cyst can damage neighboring teeth and the jawbone. Early diagnosis can prevent such problems.
How Is It Diagnosed?
Tooth cysts can be diagnosed using different methods, including the following:
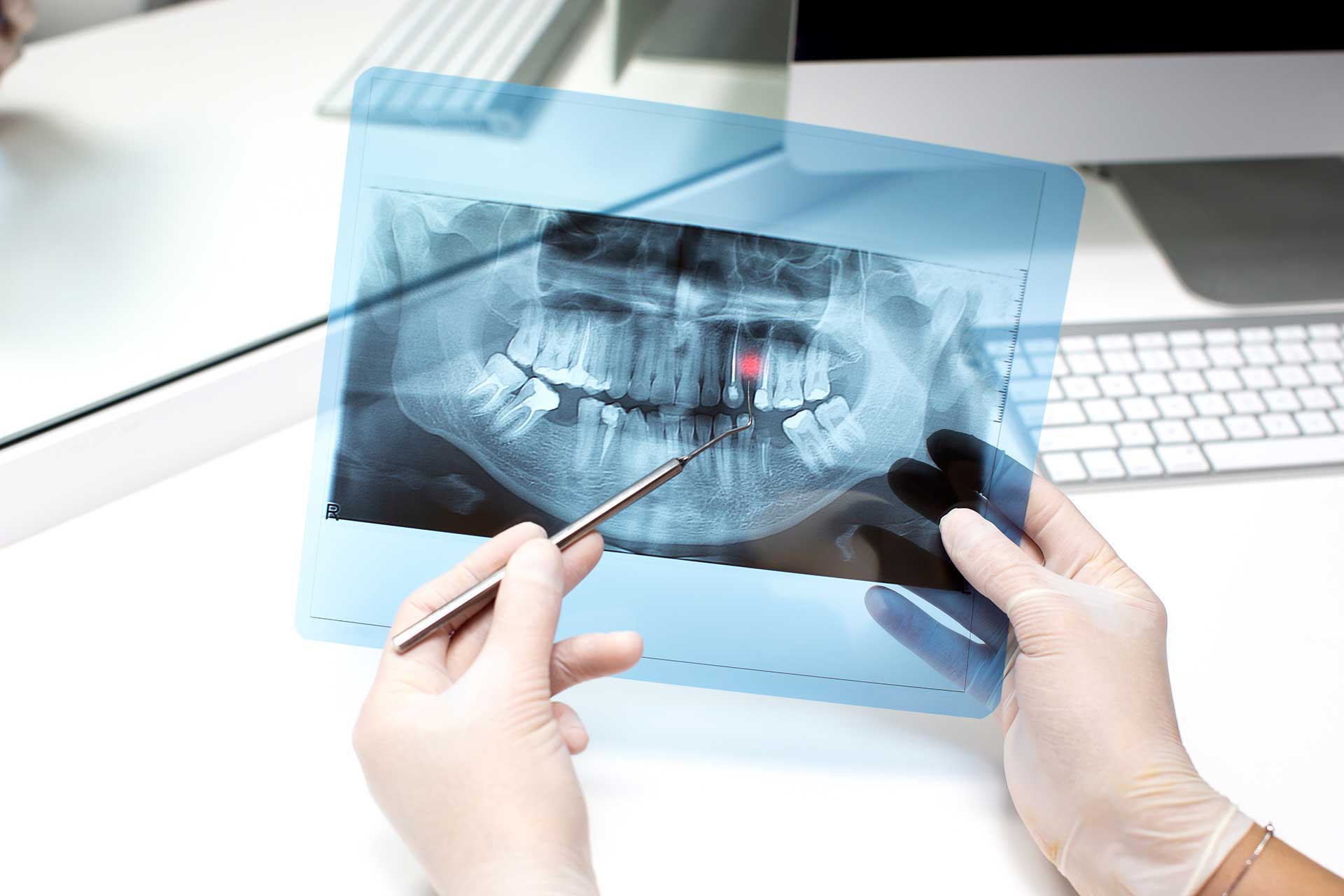
- Imaging Tests: Diagnosis is usually made using imaging tests such as X-rays or computed tomography (CT) scans. These tests can help determine the size, shape, and location of the tooth cyst.
- Clinical Evaluation: Your dentist will evaluate the symptoms and conduct a clinical examination to determine if there is a tooth cyst. Based on the results of imaging tests, an appropriate diagnosis can be made.
Treatment of Tooth Cyst
The treatment of a tooth cyst may vary depending on the situation. However, it generally includes the following steps:
- Monitoring: Small and painless cysts may be monitored by dentists to evaluate whether surgical intervention is necessary.
- Surgical Treatment: Large or infected cysts may be surgically removed. This procedure is usually performed by an oral and maxillofacial surgeon.
- Medication: Antibiotic treatment may be administered for infected cysts.
Ways to Prevent Tooth Cyst
To prevent a tooth cyst, consider the following recommendations:
- Regular Dental Check-Ups: Regular dental check-ups are important for the early detection of oral health problems such as tooth cysts. Professional examinations are important for identifying potential problems and planning treatment.
- Good Oral Hygiene: Good oral hygiene is essential for maintaining dental and gum health. Regular brushing, flossing, and mouthwash use can prevent bacterial plaque buildup and reduce the risk of tooth cyst formation.
- Avoiding Risk Factors: It is important to avoid risk factors that can increase the formation of tooth cysts. Factors such as teeth grinding, risk of trauma, and poor oral hygiene should be considered.
When symptoms are observed or discomfort such as toothache occurs, it is critical to see a dentist. Early diagnosis is important for creating an effective treatment plan. Remember, a healthy smile is not only aesthetic but also a reflection of oral and dental health.